

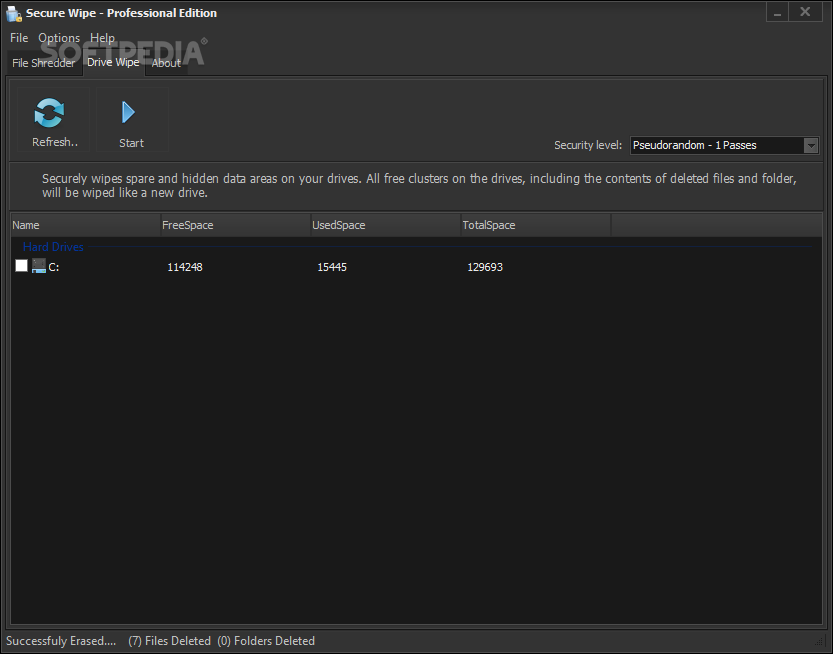
The tools are vendor specific (Corsair SSD Toolbox, OCZ Toolbox, Intel Solid State Toolbox, Samsung Magician Software). If you want to completely wipe the drive, you can use any tool supporting ATA Secure Erase, which electrically nullifies all data in the blocks. You can just make a self-expanding file to occupy all space or copy any random data just to reach 0 free space and at that point all your previous blocks are practically irreversibly erased. The result of all that is that physically, some data still exists in marked-as-empty blocks and may be theoretically recovered by special means.īut this also simplifies a lot free space erase. TRIM support enables the old blocks to be considered empty, even if they have not been erased yet, which improves endurance. The process is handled by FTL (flash translation layer) which has to do something like this when you change a very small amount of data: read one whole physical block (which let's say contains 64 pages - it can be up to 256), replace what you edited (let's say 4 pages) while keeping the rest intact (60 pages), erase a new block somewhere on the device and finally write the new set of 64 pages on that block. So if you want to erase some of the data in a block, the rest of the data will be copied to another and the initial block will be erased or marked usable/empty. Data can be written directly into an empty page, but only whole blocks can be erased. Flash memory is divided into blocks, sub-divided in pages.
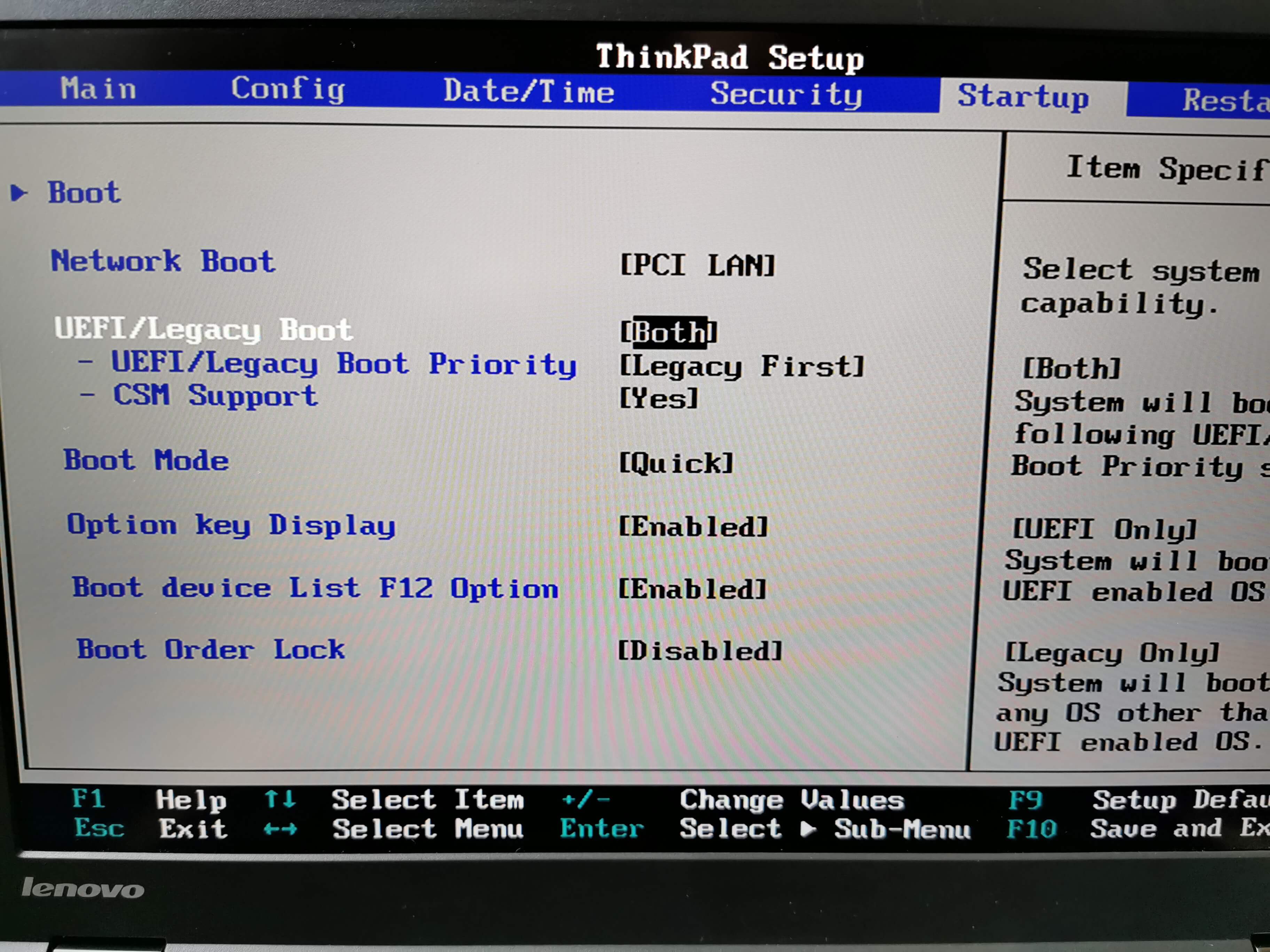
This is happening because of the internal structure. In an SSD, however, the target area must first be erased before it can be written to locations previously holding data. In an HDD system, the Operating System can request that new data be written to the same location where data is already stored, and the drive will directly overwrite the old data (magnetically).
SSD flash memory cannot overwrite existing data in a classic manner.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
